
Mobile thermal printers are carefully selected, not discovered.
Teams that deploy them at scale already know what can go wrong – undercharged batteries, driver mismatches, incompatible media, mislabelled SKUs – to name a few.
This article bypasses theory and gets straight to selection and execution: a matrix comparing the major mobile printers Triton sells and a field-tested checklist to deploy them confidently.
Start here if you’re equipping field teams or upgrading a legacy fleet.
As a leading distributor of mobile printing technology, Triton offers a curated selection of devices from top manufacturers.
Stop guessing which printer fits your operation.
We’ve analysed 18 current models across TSC Alpha and Zebra ZQ series – comparing memory configurations, battery capacities, connectivity options, and durability ratings that matter for field deployment.
The comparison matrix includes:
A mobile thermal printer is a direct thermal device for printing labels and receipts without ribbons while the user moves. While desktop thermal printers stay fixed with mains power and feed rolls for many prints, industrial printers are part of production lines, mobile thermal printers run on batteries, attach to belts and connect via Bluetooth or WiFi.
Direct thermal heads burn dots onto coated media (thermal paper), so there is no ink; Triton’s models support print widths from 48 mm to 104 mm and resolutions of 203 dpi.
The mobile thermal ecosystem is built around the printer’s width: the Alpha-2R handles 2-inch media, the Alpha30-R, Alpha-3R and 30L handle 3-inch media, the Alpha-4L, 40L and Zebra ZQ521 handle 4-inch media.
Memory options range from 32 MB to 128 MB.
Accessories include chargers, spare batteries, vehicle docks, belts and shoulder straps. Triton stocks the TSC Alpha and Zebra ZQ series, each with Bluetooth and WiFi variants and matching consumables.
Print width defines the maximum label or receipt size a mobile unit supports. Most mobile thermal printers use direct thermal technology, meaning heat activates coated media-no ribbon is required, which keeps the design simple and reliable.
The most common widths-2-inch (48 mm), 3-inch (72 mm), and 4-inch (104 mm)-stem from established standards in retail and logistics. Early point-of-sale printers used 57 mm (2 ¼ inch) and 80 mm (3 ⅛ inch) rolls, while shipping labels settled at the 102 mm (4 inch) standard, thanks to consistency in label feed mechanics and media handling equipment over decades.
Mobile printers rarely exceed 4-inch width. Wider models (6- or 8-inch) exist in industrial or desktop form factors; they demand larger batteries, chassis, and more power.
Brands Triton stocks-such as the Alpha30-R, TSC Alpha-2R, Alpha-30L, Alpha-40L, and Zebra ZQ series-stick closely to the 2-4 inch footprint to remain compact and field-ready.
The Triton catalogue aligns with this segmentation:
Yes, but only within the limits defined by the manufacturer.
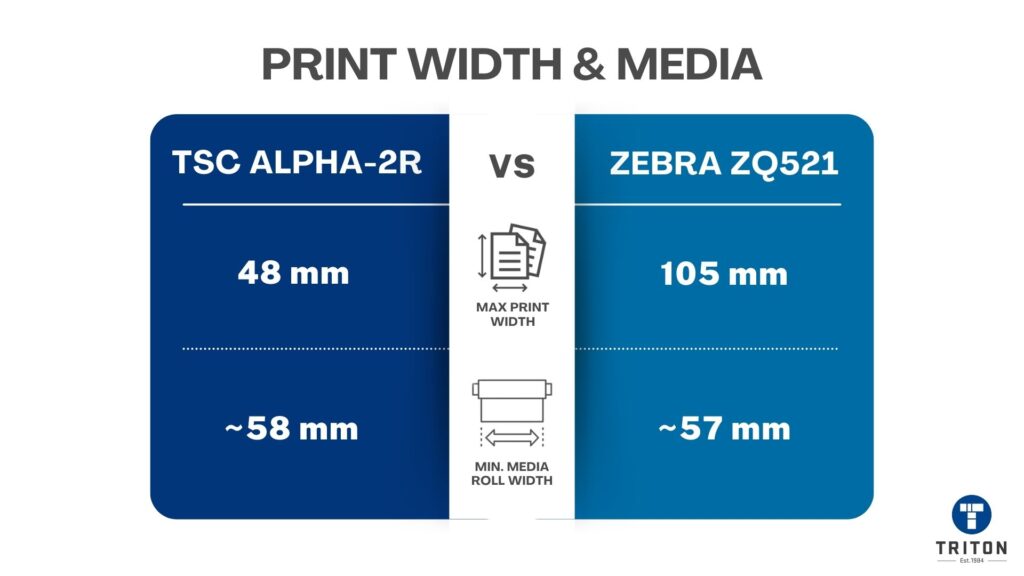
Mobile thermal printers are built with a maximum print width, yet each model specifies a minimum supported media width. The printer’s sensors won’t track the media properly if the label is narrower than this minimum. That leads to feed errors, misalignment, or incomplete printing.
The limitation is not the maximum width, but the printer’s minimum supported label width.
For example, the Zebra ZQ521 is designed for media up to 113 mm (4.45 in).
However, Zebra’s documentation lists a minimum media roll width of 57 mm (2.24 in). That means you can load media narrower than the maximum, but you cannot reliably go below that 57 mm limit. Attempting to print on, say, a 25 mm wristband would fall outside the supported range, making print quality inconsistent and feeding unreliable.
The ZQ521 also requires specific roll cores (minimum 13 mm with adapters) to align smaller rolls correctly in the chassis.
Model | Max Print Width | Minimum Media Roll Width | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
TSC Alpha-2R | 48 mm (1.89 in | ~58 mm (media) on 50 mm roll OD, requires spacers for narrower core | Narrow spacers help centre the roll for reliable feeding. |
Zebra ZQ521 | 105 mm (~4.1 in) | ~57 mm (2.24 in) roll OD; uses 0.75 in (19 mm) core adapter discs | Supports narrower media with correct core adapter. |
Most mobile thermal printers use a 203 dpi print head. That resolution balances legibility and speed, making it standard for receipts, labels and moderate-size barcodes-especially where fine detail isn’t essential.
Higher resolutions (300 dpi or 600 dpi) exist but are rare in mobile models due to speed and power consumption trade-offs.
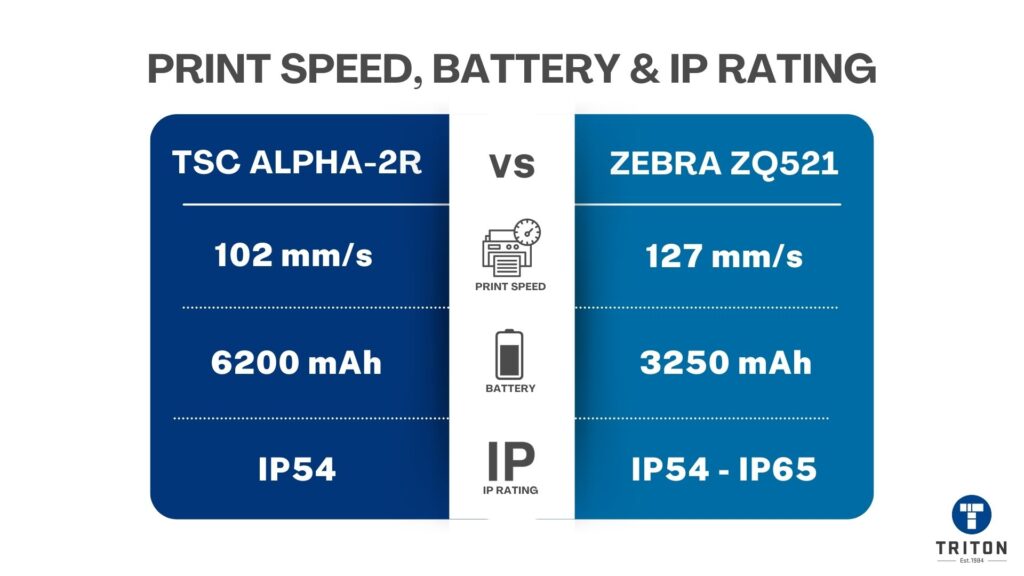
Mobile thermal printer speeds vary, but many offer print speeds between 76-102 mm/s (3-4 in/s) for compact mobile printers.
For example, the TSC Alpha-3R can print up to 102 mm/s. The Zebra ZQ511/ZQ521 prints 127 mm/s (5 in/s) at 12% print density.
Faster print speeds are available. For example, the TSC Alpha-30R (premium variant) peaks at 152 mm/s (6 in/s).
Bluetooth, which combines Classic and BLE (Bluetooth Low Energy), is the default for point-to-point work, linking one printer to one handheld computer. 802.11ac WiFi connects the printer to a network for tasks inside a building or a yard, allowing multiple users to send it jobs.
New models come with USB-C ports, which simplify charging and give a stable, wired connection for setup or in locations with wireless signal interference. NFC (Near Field Communication) is also present on some devices, but is not for printing. It makes Bluetooth pairing faster; an operator taps the device to the printer to start the connection.
The newest models also incorporate Bluetooth 5.4, introducing more secure and power-efficient communication protocols.
A printer’s power strategy is as important as the device itself. A dead battery stops all work, so your charging plan must match the job’s demands.
Don’t guess your power needs; match the battery capacity to the expected duty cycle. For example, a Zebra ZQ511 or ZQ521 printer ships with a standard 3,250 mAh battery. For longer shifts, an extended battery pack doubles that capacity.
For heavier use, TSC’s Alpha-40L uses a 6,200 mAh pack, compared to the 3,030 mAh pack in the smaller Alpha-30L.
Modern printers use a smart battery system to report their own health.
Zebra’s PowerPrecision+ and TSC’s smart Li-ion batteries report their state of charge, cycle history, and overall health through the manufacturer’s management software. This data allows a manager to identify and replace a failing battery before it causes downtime in the field.
Most mobile printers do not have a proper “hot-swap” function that controls the device without a battery. The correct procedure is a planned battery swap that takes a few seconds between tasks.
To support this, your operation needs a structured charging setup.
For operators working from vehicles all day, relying on battery swaps is inefficient.
A formal policy prevents power failures. For field teams, standardise on a three-battery system: one in the printer, one fully charged spare with the operator, and one in the depot’s multi-bay charger.
For vehicle-based teams, use battery-eliminator cradles for non-stop operation. Use the smart battery data from the vendor’s tools to check battery health every few months and replace packs that show a drop in total capacity.
Mobile printers work in warehouses, on roads, and in all weather. Durability isn’t a feature; it’s a core requirement. The ability of a printer to resist drops, dust, water, and extreme temperatures directly impacts its operational life and your return on investment. The main metrics to check are its IP rating, drop specification, and operating temperature range.
An IP rating measures how well a device’s casing protects its internal parts from solids (dust) and liquids (water). A higher number means better protection. For field use, IP54 should be your minimum standard.
For any work involving frequent exposure to rain or dust, the optional IP65 case for the Zebra ZQ500 series provides the most robust protection of these models.

A printer’s drop and tumble specifications show how well it handles physical impacts. The drop spec measures survival from a single fall onto concrete. In contrast, the tumble spec simulates hundreds of smaller, repeated falls.
If your team works on foot or from vehicle cabs where drops are likely, the Zebra ZQ511/521 offers superior drop and tumble resistance.
The safe operating temperature range is critical for any work outside of a standard room environment, especially in cold-chain logistics or outdoor work during winter.
A mobile thermal printer is useless if it cannot connect to your devices and software. You must verify its compatibility with your operating systems and check that its memory is sufficient for your print jobs and stored assets like fonts and logos.
Modern mobile printers run their own internal operating systems and provide Software Development Kits (SDKs) to help developers integrate them into business applications.
Both Zebra and TSC provide mature SDKs for Android and Windows environments. For connecting to Apple devices, however, MFi (Made for iPhone/iPad) certification is not optional; it’s a requirement for reliable pairing and communication. The Zebra ZQ500 printer family is MFi certified across the board. For TSC models like the Alpha series, MFi is often a specific SKU; confirm with the seller if it’s included in your model.
Many TSC printers also support multiple command language emulations, such as TSPL-EZ, ZPL2, and CPCL, allowing them to work as drop-in replacements for other printer brands. Command language emulation also supports backwards compatibility.
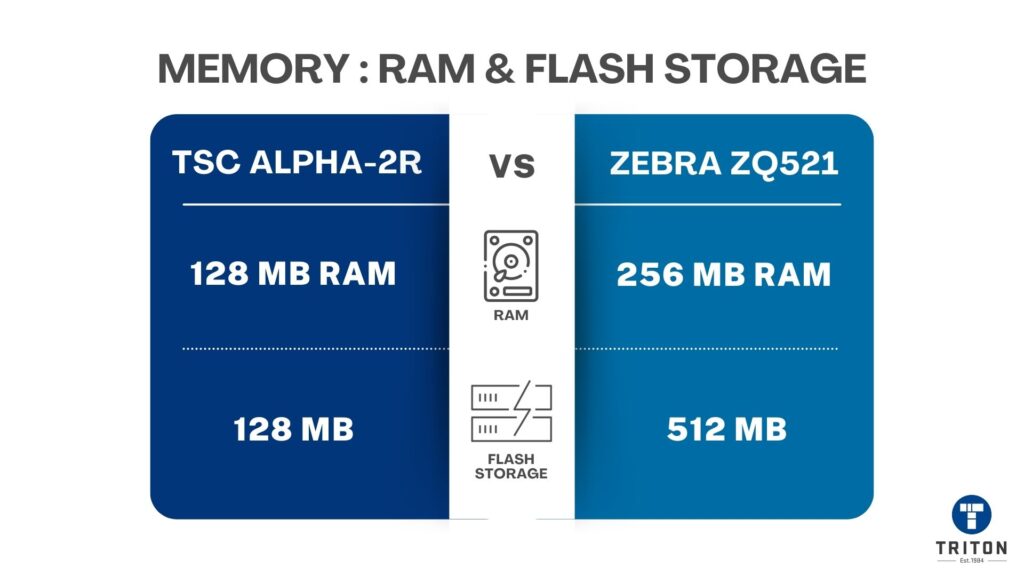
A printer uses two types of memory. RAM is a temporary buffer for processing active print jobs, with more RAM helping to render complex labels faster. Flash is permanent storage for the printer’s firmware, fonts, templates, and graphics.
Select a model with higher memory if your workflow relies on complex labels or storing many fonts and graphics on the printer itself. The microSD expansion on the TSC Alpha-30L/40L is a significant benefit for pre-loading assets onto printers before deployment, especially in large fleets. With the Zebra models, you must manage your assets to fit within the fixed user-available internal memory.
The right accessories adapt a mobile thermal printer to a specific job. A generic printer becomes a dedicated tool for vehicle, field, or specialised media work when fitted with the correct mounts, cases, and options.
For permanent installation in forklifts or other vehicles, use a manufacturer-specific vehicle cradle paired with a RAM-style mounting system. These cradles are designed to secure the printer during movement while keeping the media path and controls accessible.
Zebra and TSC offer standard shoulder straps, belt clips, and soft cases for carrying on-person. Zebra also provides a rigid exoskeleton case for its ZQ500 series, which increases drop protection while leaving all ports and media doors usable.
Your charging hardware must match your battery swap policy. For multi-shift work, stock at least one fully charged spare battery for each printer in the field.
Your charging choice depends on your workflow.
External label rewinders are for desktop printers, not mobile units. The equivalent for mobile printing is a linerless kit, a hardware modification, usually a special platen roller and print path, that allows the printer to handle adhesive labels that do not have a disposable backing liner. Linerless labels also reduce field wastage.
Zebra and TSC offer linerless-ready versions of their flagship models, including the ZQ511/ZQ521 and the Alpha-30L/40L. You must purchase the linerless-compatible version of the printer from the start and pair it with the correct linerless media.
Choosing the right accessories is straightforward. For vehicle use, select a dedicated cradle and RAM mounting components. Choose a case and strap that fit the operator’s needs for on-person work. Base your battery and charger purchases on your fleet size and shift length, ensuring you have enough spares. Finally, if you intend to use linerless media, confirm you are ordering the printer model equipped with a linerless kit.
A good routine can prevent most printing problems. Use this checklist to prepare your printers for a successful day.
Mobile thermal printer selection determines whether your field operations run smoothly or grind to a halt. The specifications matter: a 16x difference in memory between models, battery capacities ranging from 1620 to 6200 mAh, and connectivity options determining integration success or failure.
Use the matrix to match printer capabilities to your operational requirements. Don’t buy 8MB memory models for complex label formats. Don’t deploy 1620 mAh batteries for multi-shift operations. Don’t select Bluetooth-only models for enterprise WiFi environments.
The setup checklist prevents the predictable failures: dead batteries, misaligned media, and dirty printheads. Follow it consistently and most field printing problems disappear before they start.
For mobile thermal printers, desktop models, industrial systems, and all associated consumables and accessories, visit Triton Store. As Australia’s leading online destination for thermal printing technology, Triton Store stocks the complete range of TSC and Zebra printers covered in this guide, plus compatible media, replacement parts, and expert technical support to ensure successful deployment.
Whether you need a single Alpha-2R for retail operations or a fleet of ZQ521s for national logistics, Triton Store delivers the hardware, consumables, and expertise to keep your operations printing.