
High-tack labels use strong pressure-sensitive adhesives that bond strongly to hard-to-label surfaces.
These adhesives form an instant bond on contact and increase in strength over time, making removal difficult. Compared to standard permanent labels, high-tack labels offer a stronger and more reliable hold.
They perform well on rough, uneven, or porous surfaces such as wood, brick, concrete, and low-surface-energy plastics like polypropylene and polyethene. Industries such as manufacturing, logistics, electrical testing, and safety signage use high-tack labels when other pressure-sensitive adhesives fail.
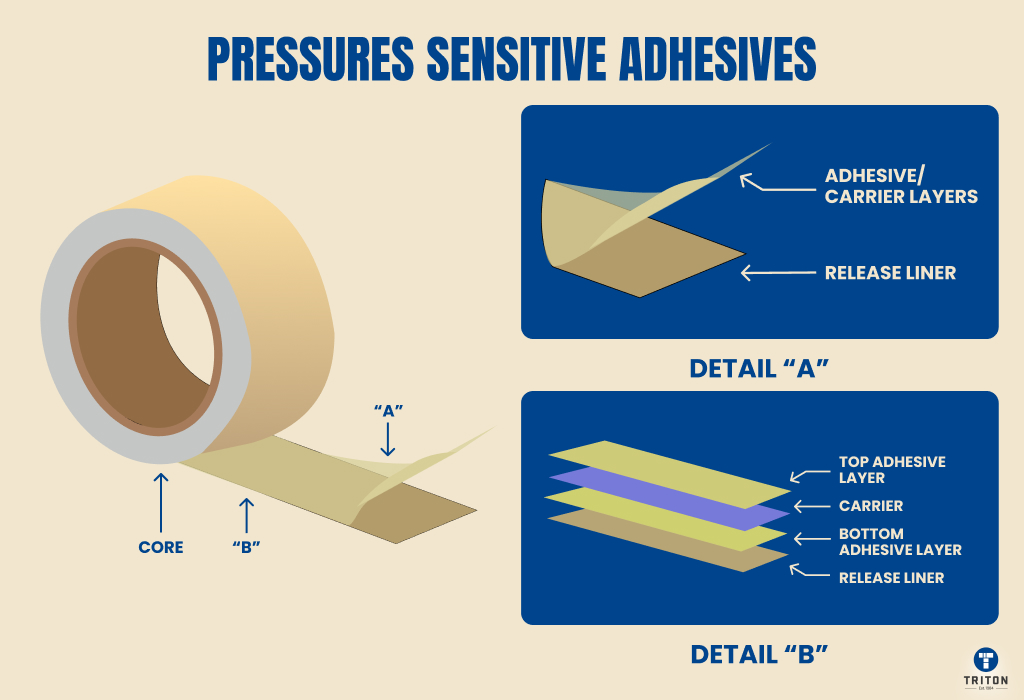
High-tack labels predominantly use Pressure Sensitive Adhesives (PSA). PSAs are non-reactive adhesives that form bonds when light pressure is applied and don’t need solvents, water, or heat. They are commonly used in products such as tapes, labels, stickers, and sticky notes. PSAs are viscoelastic and use surface contact and resistance to maintain bond strength. Their effectiveness depends on pressure applied, surface smoothness, and cleanliness. Pressure-sensitive adhesives (PSAs) are designed to function across various temperature ranges. Acrylic-based PSAs maintain adhesion between -34°C and 149°C (-29.2°F to 300.2°F), rubber-based PSAs perform effectively up to 54°C (129.2°F), and silicone-based PSAs retain adhesion from -73°C to 260°C (-99.4°F to 500°F). For optimal adhesion, most PSAs should be applied between 15°C and 35°C (59°F to 95°F). |
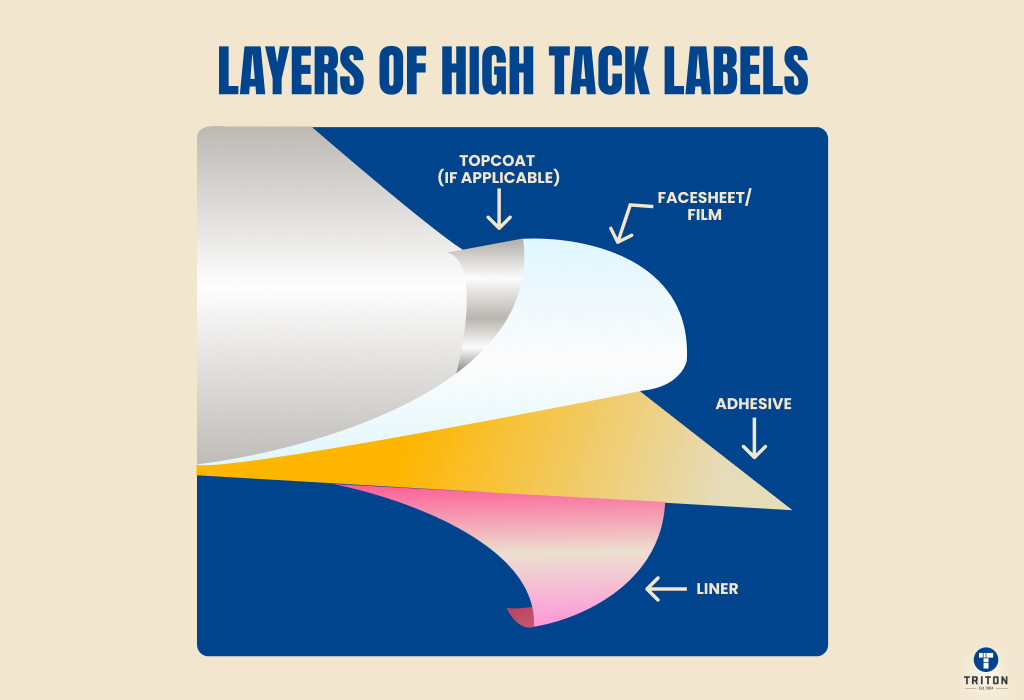
A typical high tack label consists of three main components or layers: face stock, pressure-sensitive adhesive, and release liner.
Facestock – The facestock is the printable surface. It can be paper for cost-effectiveness or synthetic (like polyester, polypropylene, or vinyl) for durability and moisture resistance. These labels usually have a facestock about 60 microns thick, offering tear and water resistance.
Adhesive – The middle layer connects the label to surfaces. High-tack adhesives are pressure-sensitive and provide strong initial and long-term adhesion. Many labels use a permanent rubber-based high-tack adhesive, which is typically 31 microns thick and works well even in cold conditions. The minimum application temperature is around -5°C.
Release Liner – The backing layer protects the adhesive and allows easy handling before application. High-tack labels often use silicone-coated liners, such as 70 gsm glassine liners, about 63 microns thick, ensuring smooth and consistent label dispensing. The total thickness of high-tack labels typically measures around 154 microns (±10%), providing a balance of flexibility and strength for industrial and packaging applications.

High tack adhesives are typically pressure-sensitive adhesives (PSAs) and fall into three main categories: rubber-based, acrylic, and silicone-based adhesives.
Rubber-based adhesives are manufactured by combining natural or synthetic rubber with tackifier resins – such as phenolic, hydrocarbon, or rosin esters – to increase stickiness.
These resins increase bonding speed by improving surface tack. Such adhesives give a strong initial grip with minimal pressure which makes them ideal for rough or low-surface-energy materials like cardboard, glass, frozen packaging, and polyolefins.
A key advantage of rubber-based adhesives is their performance in cold or moist environments. They can be sued in temperatures as low as -40°C and remain effective up to 70°C, with peel strength typically ranging from 15-25 N/25mm, depending on the surface.
These adhesives offer strong resistance to shear forces under continuous stress. At 23°C, they typically maintain their hold for 10 to 30 hours.
Acrylic high-tack adhesives are manufactured by polymerising acrylic monomers.
While their initial tack is lower than rubber-based adhesives, acrylic adhesives are more durable under harsh conditions. They are resistant to ultraviolet (UV) exposure, weathering, chemicals, and high temperatures, which makes them ideal for long-term applications.
These adhesives perform effectively across a temperature range from -50°C to 120°C, with peel strength typically between 10–20 N/25mm, depending on the substrate and bonding time.
Acrylic adhesives have high shear resistance, and maintain stable bonds under sustained stress. At 23°C, they last between 20 to 50 hours. Their tack ranges from 15–25 N/m – which is strong enough for most use cases.
Silicone-based adhesives have an inorganic structure of silicon and oxygen atoms. This gives them excellent flexibility, heat resistance, and stability in harsh chemical environments.
Unlike rubber or acrylic adhesives, silicone formulations resist breakdown under high heat and chemical exposure and maintain adhesion across a wide temperature range-from -80°C to 200°C.
They’re used in labels that must endure extreme conditions and still peel off cleanly, such as medical sterilisation labels, automotive safety labels, and aerospace components.
Silicone adhesives have lower shear resistance than acrylic or rubber types, typically lasting 5 to 20 hours at 23°C. With medium tack levels (10-15 N/m), they adhere well to low-energy surfaces.
They also hold up under exposure to harsh chemicals, solvents, and industrial cleaning agents.
They are used in industries that require strong initial tack, long-term durability, and resistance to challenging conditions.
Vehicles and automotive components have surfaces that are difficult for standard labels to adhere to. High tack labels are used for:
High-tack labels address adhesion challenges in food packaging caused by cold, wet, greasy, or rough surfaces, ensuring labels remain securely attached throughout production and distribution. Key applications include:
High tack labels play a critical role in medical and pharmaceutical applications, where labels must remain intact despite challenging surfaces and harsh conditions. Common applications include:
Feature | High Tack Labels | Standard Permanent Labels | Removable Labels |
|---|---|---|---|
Adhesion Strength | Very strong, bonds immediately | Moderate, strong but not aggressive | Low to moderate, designed for temporary adhesion |
Surface Compatibility | Works on rough, porous, low-energy surfaces | Best for smooth surfaces
| Best for smooth, non-porous surfaces |
Initial Tack | High initial tack, adheres instantly | Moderate initial tack, requires time to bond | Lower initial tack, easy to remove |
Durability | Long-lasting, resists wear and tear | Good durability but may degrade faster | Short-term use, can be repositioned |
Resistance to Moisture & Cold | Highly resistant, suitable for freezer use | Moderate resistance, may lift in cold | Limited resistance, may peel in moisture |
Resistance to Heat & Chemicals | Varies by adhesive type (rubber: lower, acrylic: higher) | Limited resistance, may degrade in heat | Poor resistance, not for harsh conditions |
Printing Compatibility | Compatible with inkjet, laser, flexo, and more | Compatible with common printing methods | Commonly inkjet and laser compatible |
Common Applications | Industrial, automotive, food packaging, safety labels | Retail, general packaging, office labelling | Retail pricing tags, temporary signage, promotional labels |
High tack labels provide strong, long-lasting adhesion for challenging surfaces where standard labels fail. Their durability, moisture resistance, and surface compatibility make them essential for industrial, automotive, food, and healthcare applications.
Need a reliable label printer? Minimise errors, speed up labelling, and improve efficiency. Visit the Triton Store today.