
RF scanners, or Radio Frequency scanners, are scanning devices that use radio waves to read and transmit data from tags or labels. These devices facilitate automated data entry, maintain accurate inventory records, reduce errors, and improve operational efficiency.
In this article, we will explore the different types of RF scanners and how RF scanning systems work. We’ll also discuss the benefits of using RF scanners in warehouses, compare RF scanning with RFID, and provide guidance on choosing the right RF scanner for your needs.
RF scanners have come a long from their World War II origins to become versatile tools in supply chain management. These scanners can be broadly categorised into two types.
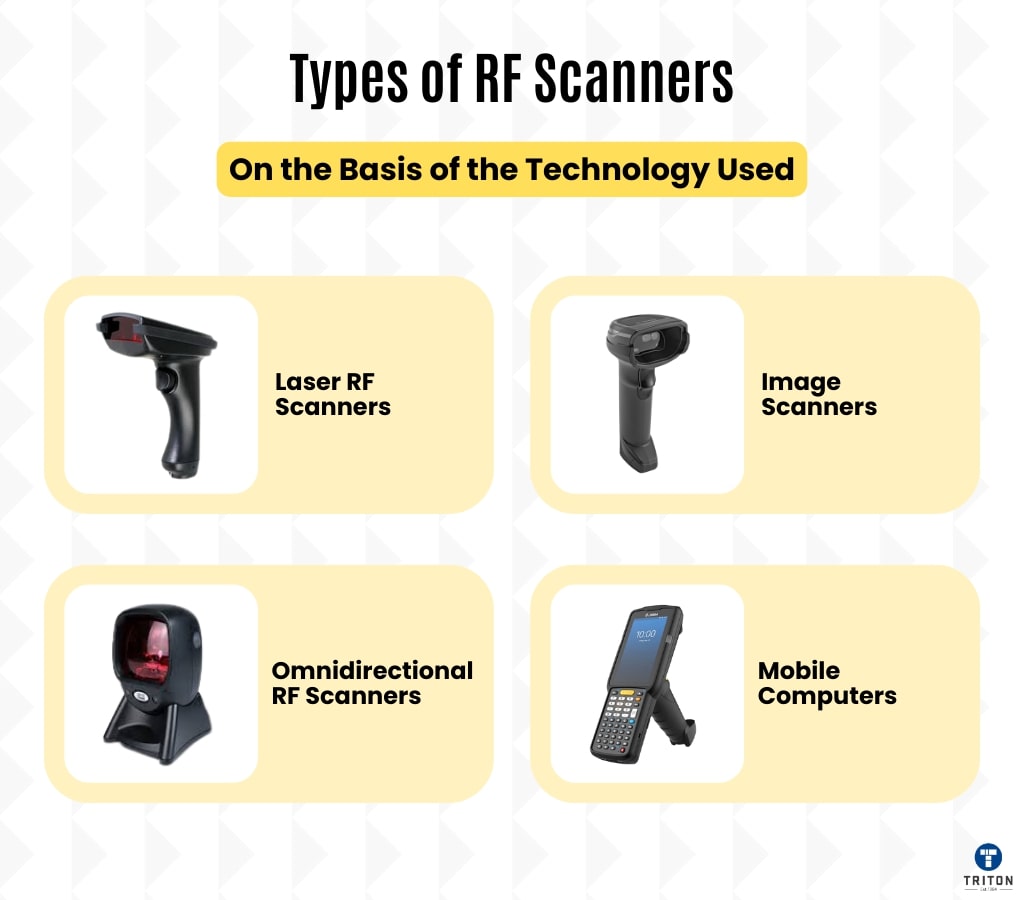
RF scanners utilise different technologies to read and transmit data from tags or labels. Here are the main types based on the technology used:
Laser RF scanners use laser beams to read barcodes and transmit the data via radio frequency.
Here’s how they work: The scanner emits a laser light that shines on the barcode. The barcode’s black-and-white patterns reflect the laser. The reflected light intensity varies depending on whether the laser hits the white or black part of the barcode.
A photodiode inside the scanner captures this reflected light. The photodiode then converts the reflected light into an electrical signal, which it processes to decode the information stored in the barcode.
Key Features
Limitations:
Use Case:
Laser RF scanners are a reliable choice for many warehousing applications due to their speed and accuracy, especially when dealing with standard 1D barcodes. They are ideal for environments where quick and precise scanning is needed, such as inventory tracking and shipping processes.
Image scanners, also known as camera-based scanners, use imaging technology to capture a picture of the barcode and then decode it.
These scanners use a small camera to take a snapshot of the barcode. This barcode image is then analysed to extract the information.
Key Features:
Limitations:
Use Case:
Image scanners are ideal for use cases where both 1D and 2D barcode types must be scanned. They are particularly useful in warehouses that handle products with barcodes on curved or reflective surfaces, such as bottles or shiny packaging.
In dynamic environments where products are moving, such as on conveyor belt systems, they ensure accurate and efficient scanning.
Mobile computers, also known as mobile terminals, are devices that combine the scanning capabilities of RF scanners with the functionalities of handheld computers.
These devices are designed to scan barcodes and allow users to process and manage data directly on the device. They are equipped with Windows or Android operating systems, touchscreens, and multiple connectivity options, making them powerful tools for inventory management, other warehouse tasks, and Industry 4.0.
Key Features:
Limitations:
Use Case:
Mobile computers are ideal for environments where workers must perform multiple tasks, such as scanning, data entry, and communication, all on a single device. They are beneficial in large warehouses and distribution centres where real-time data access and processing are paramount.
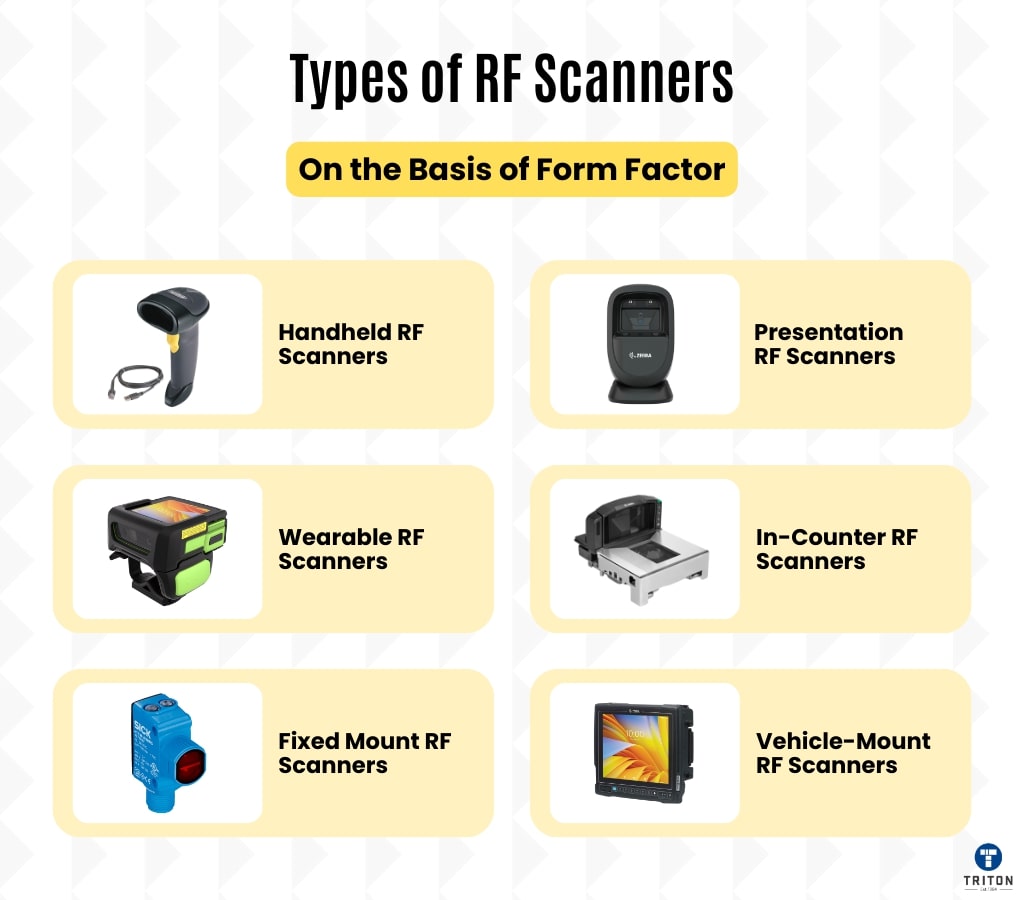
RF scanners can also be categorised based on their form factor, which refers to their physical design and how they are used. Here are the main types:
Handheld RF scanners are portable and easy to use. A trigger mechanism activates the scanning function, simplifying operation. These scanners can handle items of various sizes and shapes and allow users to move freely across different areas.
Handheld laser scanners are built to withstand drops and rough handling, which makes them durable in demanding warehouse environments.
On the downsite, manual operation is less efficient for high-volume scanning tasks. Frequent use can also lead to quick battery depletion, requiring regular recharging or battery replacements. Despite these limitations, handheld RF scanners remain popular due to their versatility and ease of use.
Presentation RF scanners, also called On-Counter scanners, are designed for hands-free operation.
These devices are typically mounted on a stand or placed on a counter, allowing users to present the barcode in front of the scanner for automatic reading. Presentation RF scanners don’t require manual activation, making the scanning process simple.
Presentation RF scanners provide a stationary solution for handling a continuous flow of items. They are particularly useful at retail counters or customer service areas where quick, hands-free scanning is beneficial.
However, their fixed position means they are not suitable for scanning items that are not easily brought to the scanner, such as large furniture. Also, they require a dedicated space on a counter or stand, which is not ideal in environments with limited space.
Wearable RF scanners are designed to be worn by the user, typically on the hand, wrist or finger. These devices enable workers to scan items while keeping their hands free for other tasks, such as picking, packing, and sorting operations.
Wearable RF scanners are used in shipping and logistics, where workers must perform repetitive scanning tasks and continuously handle items.
Despite their advantages, their small size limits battery life and scanning range. The initial cost of wearable RF scanners is also higher than traditional handheld models.
In conclusion, wearable RF scanners offer significant benefits in terms of mobility and convenience. They are a popular choice in high-paced, hands-on work environments.
In-counter RF scanners are built directly into the counter or checkout area, providing a seamless and integrated scanning solution. These scanners are found in retail settings, such as grocery stores and supermarkets, where high-volume scanning is required.
In-Counter RF scanners are designed for high efficiency. They allow users to quickly pass items over the scanner without needing to manually align the barcode. The scanners are also durable and can withstand the wear and tear of constant use.
However, in-counter RF scanners’ fixed installation means they are not portable and can only be used at their designated location. They also require a significant upfront investment and installation.
Fixed-mount RF scanners are stationary devices mounted in a fixed position, often on walls, conveyors, or production lines. These scanners are designed to read barcodes automatically as items pass by, without manual handling.
Fixed-mount RF scanners are ideal for high-volume and automated environments, such as manufacturing plants and large warehouses. They provide continuous scanning capability, ensuring every item is accounted for without slowing down the process.
Vehicle-mount RF scanners are designed to be mounted on warehouse vehicles like forklifts, pallet jacks, and carts. These scanners provide mobility and efficiency by allowing operators to scan items directly from their vehicles without dismounting.
Vehicle-mount RF scanners are ideal for large warehouses and distribution centres where operators need to quickly move large quantities of goods. These scanners enhance productivity by integrating scanning tasks with vehicle operation, reducing the time and effort required to manually scan items.
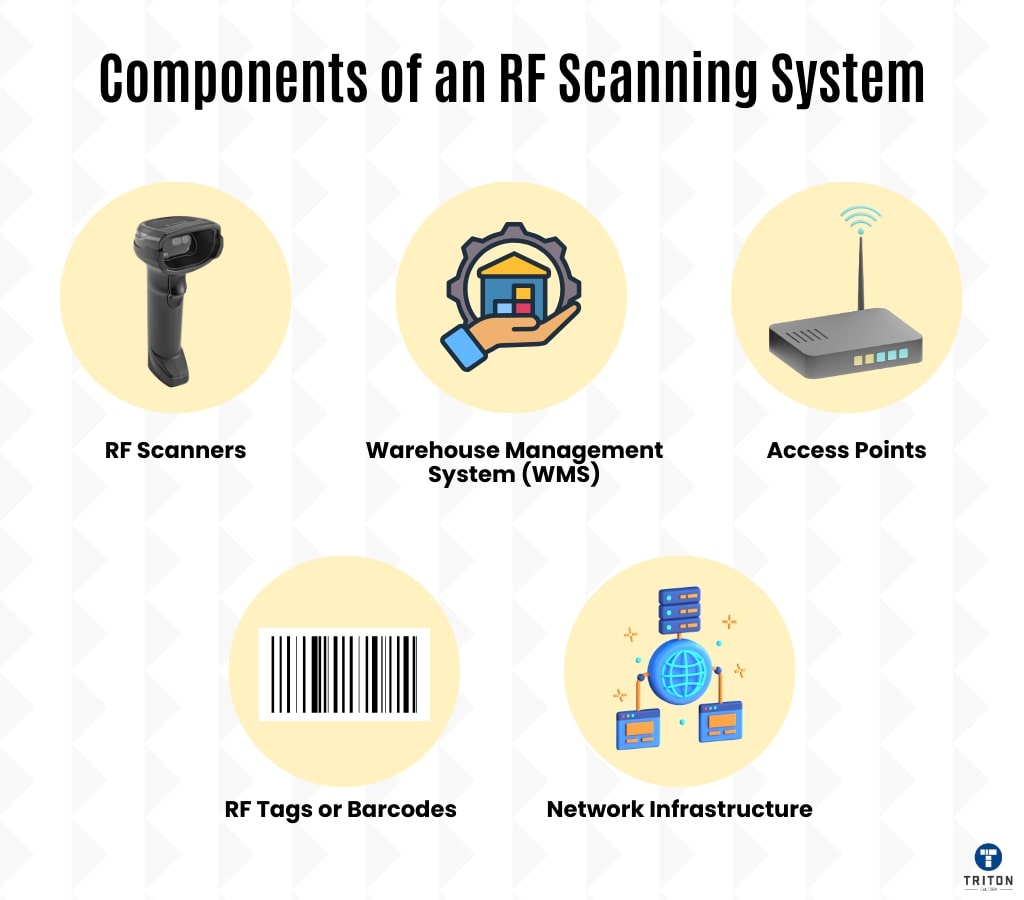
An RF scanning system is a comprehensive setup that utilises RF scanners to read and transmit data from barcodes or tags. This system is integral to modern warehouse and inventory management, offering a streamlined approach to tracking and managing stock.
An RF scanning system typically consists of the following components:
RF scanning involves a series of steps that allow data to be read from barcodes or tags and transmitted to a central database for processing. Here’s a breakdown of how RF scanning works in a typical warehouse setting.
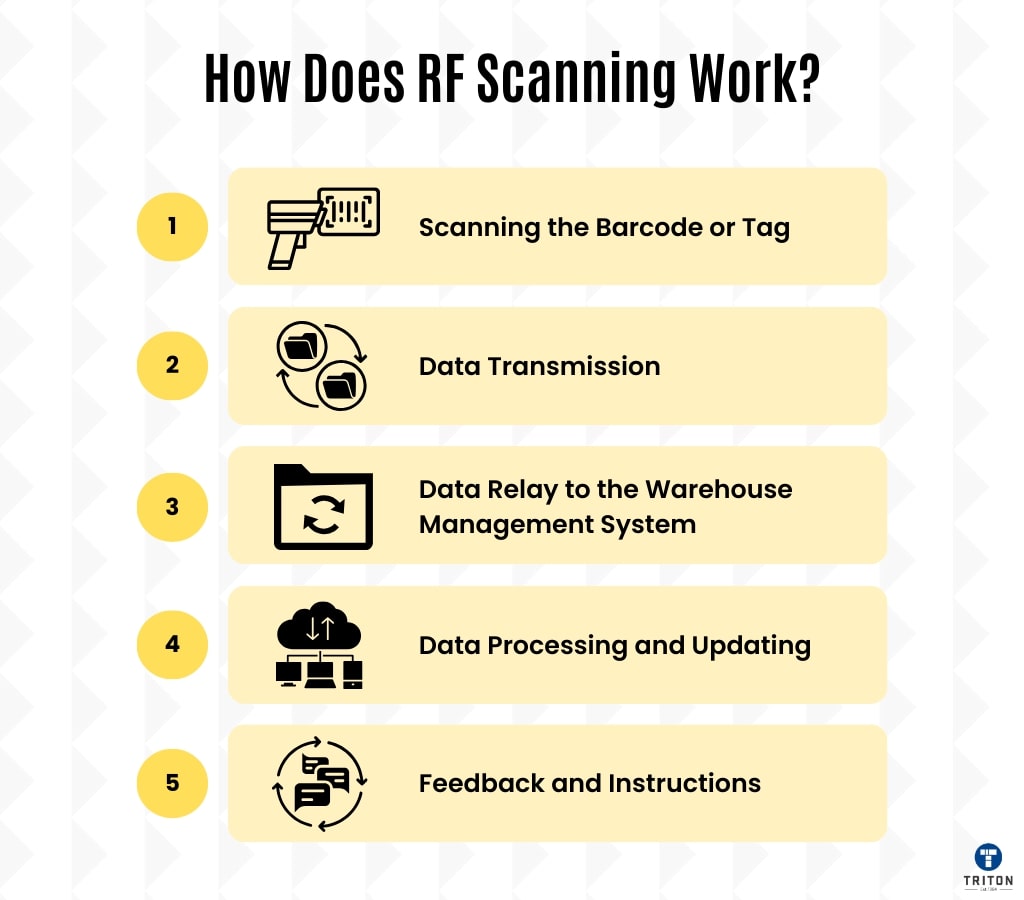
The scanning process begins by pointing the RF scanner at a barcode or tag and pulling the trigger.
At their core, RF scanners utilise a combination of light sources, such as LEDs or a laser beam, to illuminate the barcodes or tags. These barcodes or tags absorb some light and reflect the remaining light.
The scanner’s sensor detects the reflected light and captures it, converting it into an analogue signal. This signal is then sent to the scanner’s decoder, translating it into digital data. This digital data represents the information encoded in the barcode or tag and is stored in the scanner.
This entire process is very quick, typically taking just a fraction of a second, allowing for rapid and efficient scanning.
Once the barcode or tag is scanned, the data is transmitted wirelessly to an access point. This is done through the wireless network connection that links the scanner to the warehouse’s network infrastructure.
The access point receives the data from the scanner and relays it to the Warehouse Management System.
The WMS processes the scanned data, updating inventory records in real-time. It tracks the location, quantity, and status of each item, ensuring accurate and up-to-date inventory management.
Based on the scanned data, the WMS can provide feedback and instructions to the warehouse staff. For instance, it might indicate where to place a scanned item or notify staff if inventory levels are low and need replenishing.
Example Scenario: A warehouse worker scans a barcode on a pallet of goods using a handheld RF scanner. The scanner captures the data and transmits it to a nearby access point. The access point sends the data to the WMS, which updates the inventory records to reflect the new arrival. The WMS then directs the worker to place the pallet in a specific location within the warehouse.
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) and RF (Radio Frequency) scanning are two distinct technologies used for tracking and managing inventory. While both utilise radio frequency to transmit data, their methods, applications, and functionalities differ significantly.
The table below highlights the key differences between RF and RFID scanning.
Feature | RFID | RF Scanning |
|---|---|---|
Technology | Uses radio waves to communicate with tags | Uses light (laser or LED) to read barcodes
|
Scanning Range | Can read tags from a few centimetres to several metres, depending on the tag type and reader
| Requires close proximity within a few inches to a couple of feet. |
Line of Sight | Does not require a direct line of sight | Requires direct line of sight |
Tag/Label Type | RFID tags (passive, semi-passive or active) | Printed barcodes |
Implementation | Requires specialised equipment and software, potentially more complex to set up | Easier to implement with standard barcode scanners and existing infrastructure |
Interference | Affected by electromagnetic interference and metal objects | Less susceptible to interference |
Speed | Can read multiple tags simultaneously
| Reads one barcode at a time |
Cost | Generally higher due to the cost of RFID tags and readers. Can cost up to $50 per tag | More cost-effective (a few cents per label) |
Applications | Inventory management, asset tracking, access control, supply chain management | Warehouse management, retail checkout, shipping and receiving, inventory audits |
RF scanners significantly improve the accuracy of inventory tracking by automatically capturing data from product labels. This automation reduces the risk of manual entry errors, ensuring precise inventory records.
In warehouses, this accuracy translates to better stock management, reducing discrepancies and preventing issues like stockouts or overstock situations.
RF scanners allow workers to perform tasks such as locating, picking, and packing items more quickly and with less effort. This increased efficiency means workers can handle more tasks in the same amount of time.
RF scanners provide comprehensive data collection capabilities, capturing detailed information about each item scanned. This data is instantly transmitted to the warehouse management system, which updates inventory records in real-time.
This real-time visibility into inventory levels allows warehouse managers to make informed decisions quickly, such as reallocating resources or adjusting stock levels. Enhanced reporting capabilities also provide valuable insights into inventory trends, helping to optimise warehouse operations and improve overall efficiency.
RF scanners facilitate better inventory management by providing accurate and up-to-date information on stock levels. Improved inventory accuracy also supports better planning and forecasting, ensuring that the right amount of stock is available to meet demand.
Additionally, the ability to track the movement of items within the warehouse enhances the overall organisation and management of stock. This leads to more efficient use of warehouse space and resources
Manual data entry is prone to errors, leading to significant issues in inventory management. RF scanners eliminate much of the manual entry process, reducing the likelihood of mistakes.
This accuracy is particularly important in a warehouse setting, where errors can lead to misplaced items, incorrect shipments, and costly returns. By reducing human error, RF scanners contribute to smoother and more reliable warehouse operations.
The speed at which RF scanners can read and process data is much faster than manual entry. This rapid scanning capability reduces processing times for receiving, picking, packing, and shipping items.
This acceleration leads to quicker order fulfilment and improved operational efficiency, which are necessary for maintaining a smooth warehouse workflow.
RF scanning systems are scalable, allowing warehouses to add more scanners as operations grow without disrupting existing workflows. This scalability ensures that the system can handle increased volumes efficiently.
Here’s how RF scanning is used in various warehousing processes.
When new inventory arrives at the warehouse, workers use RF scanners to quickly scan the barcodes on the goods. This process automatically updates the warehouse management system with the received quantities, ensuring accurate and immediate inventory updates. It also helps verify that the items received match the purchase orders.
After receiving goods, they need to be placed in designated storage locations.
Workers scan the items and the storage location barcodes using RF scanners. This ensures the WMS tracks the exact location of each item, making future retrievals more efficient.
In the order-picking process, workers use handheld or wearable RF scanners to scan items as they pick them for orders. This practice ensures that the correct items and quantities are picked, reducing errors and improving order accuracy. Real-time data updates maintain an accurate inventory count and streamline the picking process.
Regular cycle counts are essential for maintaining inventory accuracy. RF scanners make this process more efficient by allowing workers to quickly scan and count items in specific warehouse areas.
The data is instantly updated in the WMS, ensuring that inventory records remain accurate without manual counting and data entry.
During the shipping process, RF scanners verify that the correct items are being packed and shipped to customers. This reduces the risk of shipping errors and enhances customer satisfaction.
When items need to be moved from one location to another within the warehouse, RF scanners track these movements. Scanning the items and their new locations updates the WMS in real-time, maintaining accurate records and minimising misplaced items.
Handling returns efficiently is crucial for warehouse operations. RF scanners streamline returns by quickly scanning returned items and updating the WMS with their status. This helps in sorting and restocking the items promptly, reducing the time it takes to process returns and get the items back into inventory.
RF scanners track the usage and location of warehouse equipment, such as forklifts and pallet jacks. Attaching tags to equipment and scanning them regularly allows warehouses to monitor status, usage patterns, and maintenance needs. This helps manage equipment effectively, ensuring availability and proper maintenance to avoid downtime.
The cost of RF scanners can vary widely based on several factors, including the type of scanner, its features, and the manufacturer. Generally, the price of RF scanners can range from $100 to $4,000.
Several key factors influence the cost:
In addition to the purchase price, it’s essential to consider other expenses such as maintenance, repairs, and training. Regular maintenance and potential repairs can add to the total cost of ownership. Training staff to use RF scanners effectively might incur costs, especially if the devices are complex or if there is a significant change from previous systems.
When budgeting for RF scanners, consider the total cost of ownership, not just the upfront purchase price. Investing in higher-quality, more durable scanners may result in lower long-term costs due to reduced maintenance and replacement needs.
Choosing the right RF scanner for the warehouse significantly impacts efficiency and productivity. Here are some key considerations to help you make the best choice.
Identify the specific requirements of your warehouse operations. Consider the types of items you need to scan, the environment in which the scanners will be used, and the volume of scanning required.
Understanding your needs will help narrow down the options.
Different types of RF scanners are suited for different tasks:
Consider the types of barcode labels you need to scan. Some scanners can read both 1D and 2D barcodes, while others may specialise in one type.
Additionally, evaluate the scanning range required for your operations. Some scanners are designed for close-range scanning, a few inches away, while others can read barcodes from several feet away or more.
Ensure the scanner’s capabilities match the barcode symbologies and distances you’ll encounter in your warehouse operations.
Evaluate the durability of the scanner, especially if it will be used in harsh environments. Look for rugged scanners that can withstand drops, dust, and moisture.
Ergonomics is also important, as comfortable and easy-to-use scanners can reduce worker fatigue and increase productivity.
Ensure the RF scanner can easily integrate with your existing warehouse management system or enterprise resource planning (ERP) software. Consider the connectivity options, such as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, or cellular connections, to ensure seamless data transmission.
For handheld and wearable scanners, battery life is a crucial factor.
Long battery life reduces downtime and ensures the scanners can operate throughout the workday without frequent recharging or battery replacements.
Determine your budget for purchasing RF scanners. While finding cost-effective solutions is essential, investing in higher-quality scanners can save money in the long run by reducing maintenance and replacement costs.
Choose a reputable retailer that offers good customer support and a comprehensive warranty. Reliable support helps resolve issues quickly and minimise downtime, while a solid warranty can protect your investment.
Consider the ease of use of the scanners and the availability of training resources. User-friendly scanners with adequate training can help your staff get up to speed quickly and ensure efficient operation.
RF scanners can read various 1D barcodes and 2D barcodes. Some RF scanners can also read RFID tags, which store more data and offer longer read ranges.
An RF detector can detect radio frequency wireless network signals emitted by devices such as RF scanners, RFID tags, and wireless communication devices. It is used to identify the presence and strength of these signals in a given area.
Most RF scanners can integrate with a wide range of Warehouse Management Systems. Still, compatibility depends on the scanner’s software and the WMS platform. It’s important to verify integration capabilities with your specific WMS before purchasing.
The lifespan of RF scanners varies based on usage, maintenance, and build quality. Generally, RF scanners can last from three to five years with proper care and maintenance. High-quality, rugged models designed for industrial use may last longer.
Apart from warehouses, RF scanning is used in various industries, including retail for inventory control & management, healthcare for patient and equipment tracking, manufacturing for production line management, logistics for tracking shipments, and libraries for cataloguing books.
Auckland
Christchurch
Phone 09 579 2057
Live Chat – Widget below
Auckland
Christchurch
Phone 09 579 2057
Live Chat – Widget below