
Returns are a common part of the eCommerce experience.
According to the National Retail Federation, total eCommerce returns amounted to $743 billion in 2023, with a return rate of 14.5% of total sales. This data highlights the vast scale of returns that eCommerce needs to manage.
To handle these returns efficiently, businesses use Return Merchandise Authorisation (RMA).
RMA, also known as return authorisation (RA) or return goods authorisation (RGA), is an alphanumeric code a business assigns to a product to authorise a return.
In this article, we’ll dive into what RMA is and break down the structure of RMA labels. We’ll also discuss where RMA is used, how it works, and the differences between RMA, shipping labels, and serial numbers. Finally, we’ll cover the benefits of using RMA and explain who should implement RMA systems.
RMA labels that an RMA code which is used to authorise, identify, manage, and track returned products. These labels are affixed to products being returned for refunds, replacements, or repairs.
In addition to the RMA code, the label includes information like the customer’s details, the original shipping address, the return shipping address, and the tracking number.
RMA labels ensure that returned items are processed efficiently and accurately, reducing errors and streamlining the workflow. Using RMA labels helps businesses maintain better control over their inventory. It also improves customer satisfaction by handling returns promptly and correctly.

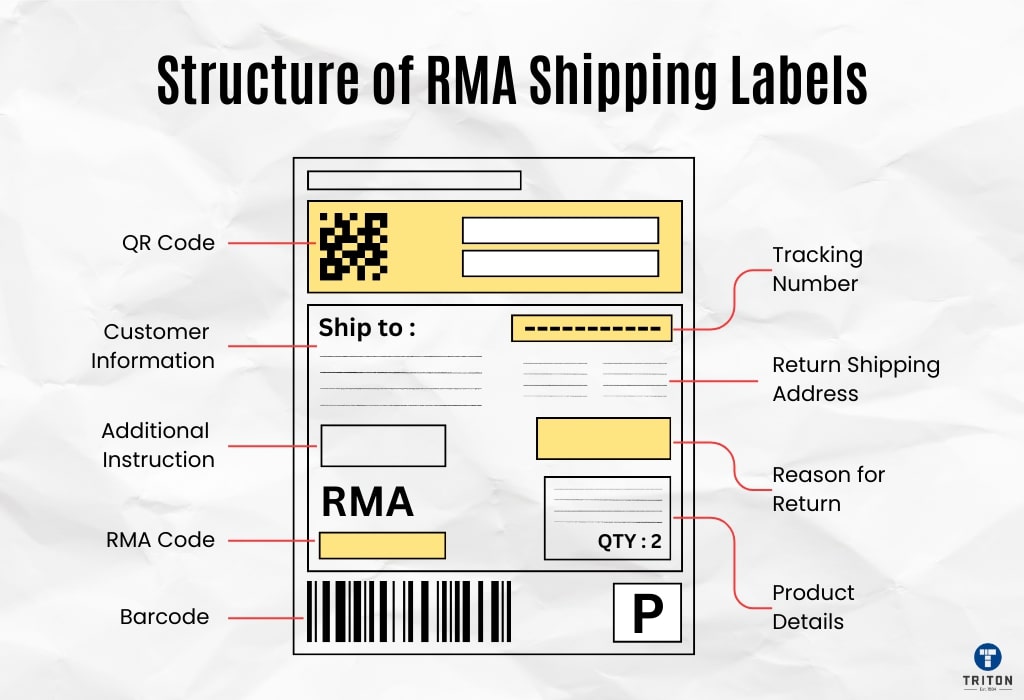
RMA shipping labels are designed to include key pieces of information that ensure the return process is smooth and efficient. Each label component plays a specific role in managing and tracking returned products.
There is no standard format for RMA labels, and different businesses may use different formats.
However, some common components are usually included, such as.
Return Merchandise Authorisation is used to manage different types of product returns efficiently. Here are some common uses of RMA.
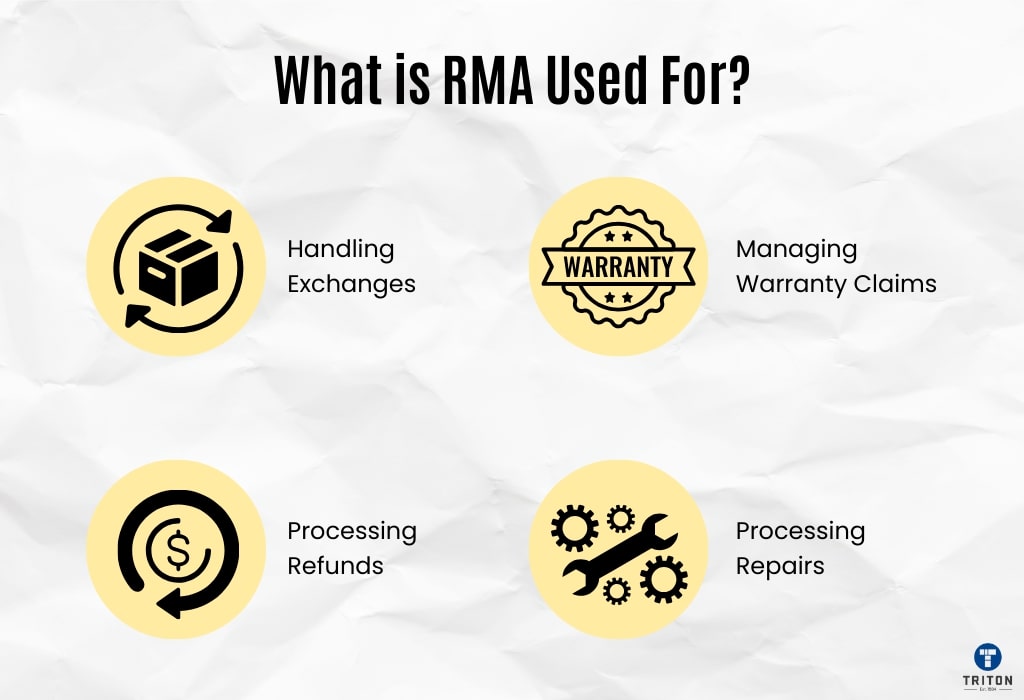
RMAs are often used to process refunds when customers return products they no longer want. The RMA system helps businesses track these returns, verify the condition of the returned items, and issue refunds promptly.
This ensures a smooth and transparent refund process, enhancing customer satisfaction.
Customers sometimes return products to exchange them for different items. RMAs facilitate this process by providing a structured way to manage the exchange, track the returned product, and ensure that the replacement item is shipped out correctly. This helps in maintaining accurate inventory and ensuring customers receive the correct products.
RMAs are crucial for processing warranty claims. When a product fails or malfunctions within the warranty period, customers can return it for repair or replacement. The RMA system helps businesses verify warranty coverage, track the return, and manage the repair or replacement process efficiently.
RMAs are used when customers return products for repairs, either within or outside the warranty period. The RMA label includes details about the issue, allowing the repair department to quickly identify and address the problem. This streamlines the repair process and ensures timely service.
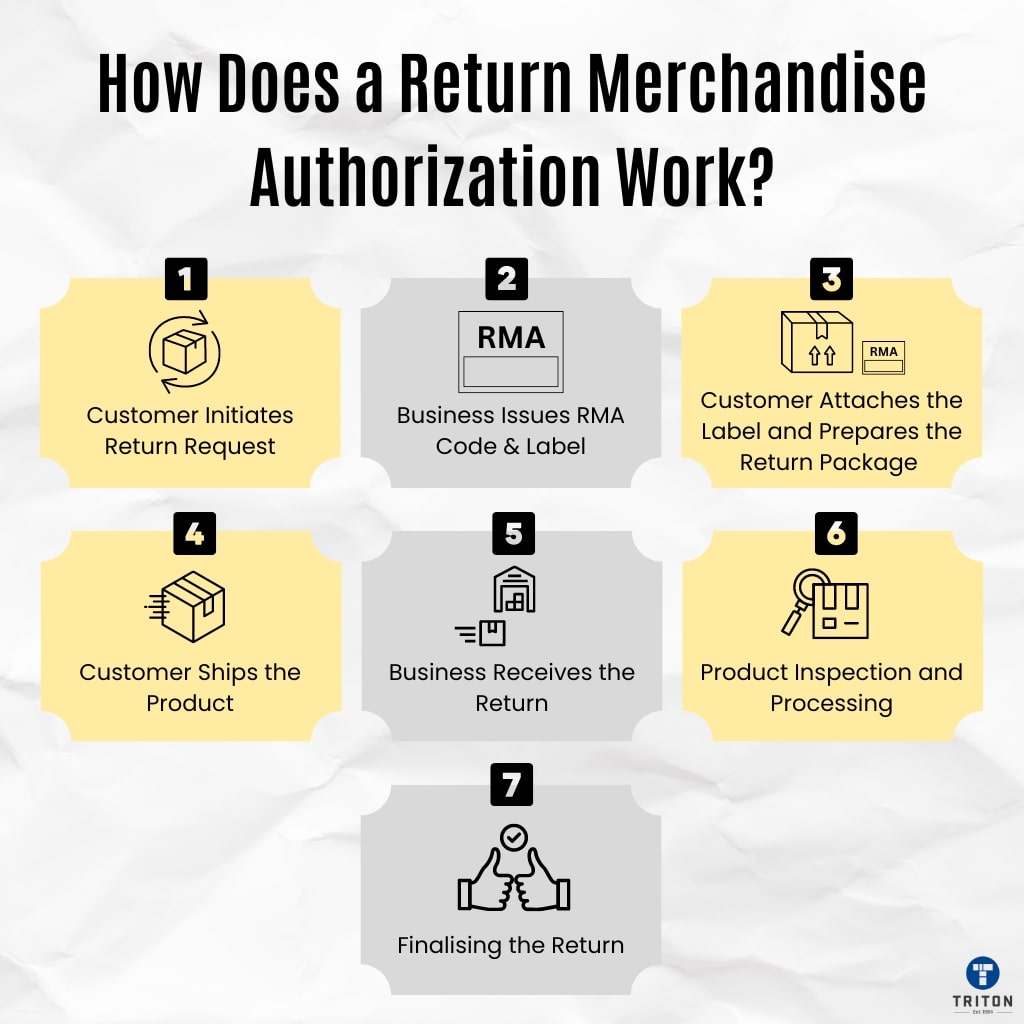
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how an RMA typically works.
The process begins when a customer decides to return a product. They contact the business through customer service, an online portal, or an email to request a return. The customer provides details about the product and the reason for the return.
After reviewing the return request, the business generates an RMA code. This unique alphanumeric code is assigned to the specific return request. The RMA code, along with the label, is then communicated to the customer, usually via email or through the online account.
The customer prints and attaches the RMA label to the return package. The package is prepared according to any specific instructions provided by the business.
The customer sends the return package to the address specified in the RMA label. The package can be tracked using the tracking number provided, ensuring both the customer and the business can monitor its progress.
Upon receiving the return package, the business scans the RMA label using a barcode scanner to retrieve the RMA code and associated details. The return is logged into the system, and the package is forwarded to the appropriate department (e.g., inspection, repair, or restocking).
The returned product is inspected to verify its condition and the reason for return. Depending on the outcome of the inspection, the business proceeds with the next steps, such as issuing a refund, sending a replacement, or repairing the product.
Once the return is processed, the customer is notified of the outcome. If a refund is issued, it is credited back to the customer’s original payment method.
For exchanges or replacements, the new product is shipped to the customer. In the case of repairs, the repaired product is returned to the customer.
The RMA system updates the business’s records to reflect the completed return. This helps maintain accurate inventory levels and provides valuable data for analysing return trends and identifying potential product issues.
RMA labels and shipping labels are both essential components in the logistics of product handling, but they serve distinct purposes. Here is a table summarising the differences between a shipping label and an RMA label.
Aspect | RMA Label | Shipping Label |
|---|---|---|
Purpose | Authorises product returns | Directs the shipment of products to a destination |
Contents | RMA code, customer info, return address, product details, reason for return, tracking number, additional instructions | Recipient address, sender address, weight, dimensions, tracking number, shipping method
|
Usage | Used for managing and authorising returns
| Used for sending products from one party to other |
Issued By | Issued by the business to the customer | Issued by the shipping carrier (e.g., FedEx, UPS)
|
Scanning | Often includes a barcode or QR code for quick scanning and processing
| Includes a barcode for tracking and delivery purposes |
Tracking | Tracks the return process and ensures the return is processed accurately | Tracks the shipment from the origin to the destination
|
Here’s a comparison highlighting the differences between a serial number and an RMA.
Aspect | RMA | Serial Number |
|---|---|---|
Purpose | Authorises and tracks product returns | Uniquely identifies an individual product |
Usage | Used for managing and authorising returns | Used for product lifecycle tracking and inventory management |
Issued By | Issued by the business to the customer | Assigned by the manufacturer at the time of production |
Tracking | Tracks the return process and ensures accurate processing
| Tracks the product’s history, including manufacturing, sales, and repairs
|
Scanning | Often includes a barcode or QR code | Does not include a barcode |
Labelling | Usually printed on RMA labels | Printed or engraved during production |
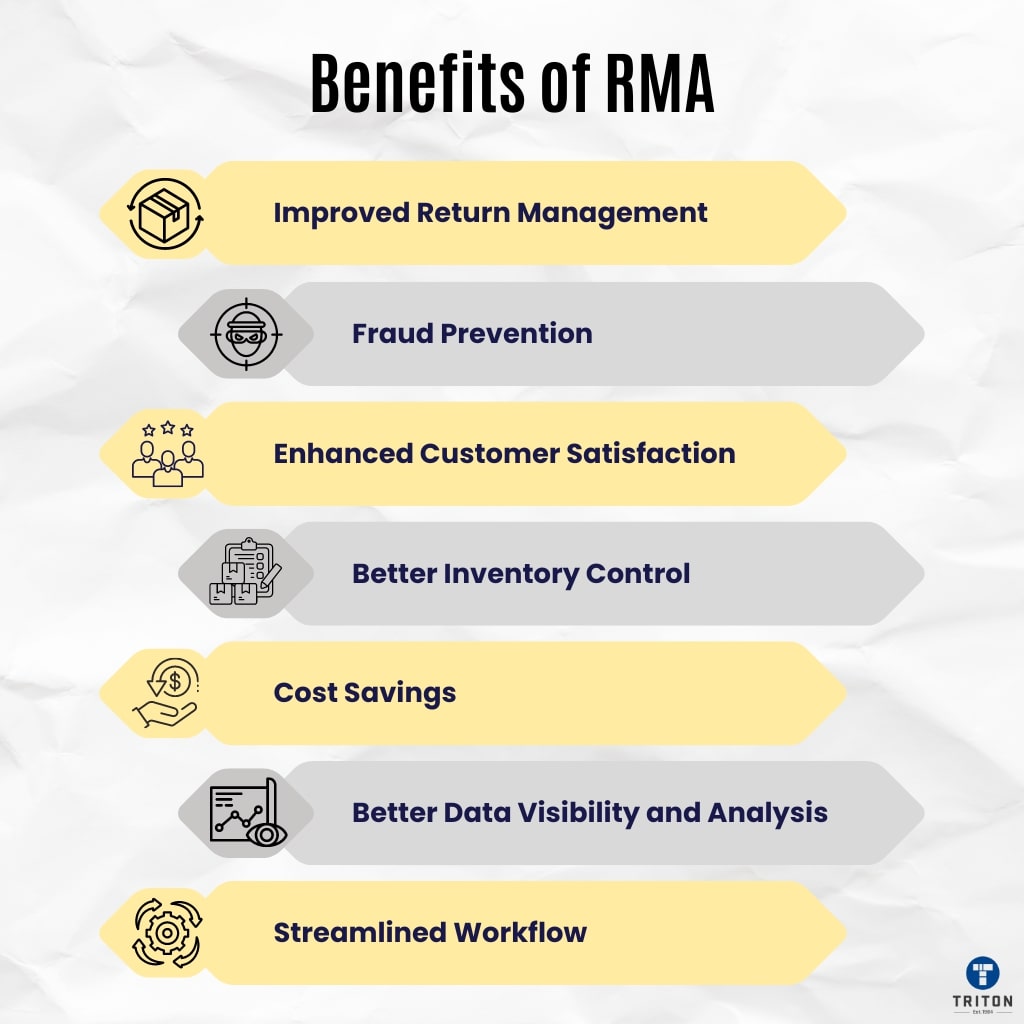
Implementing a Return Merchandise Authorisation system offers several advantages for eCommerce businesses.
An RMA system allows businesses to manage returns systematically. Issuing RMA codes and using RMA labels enable companies to track and process returns accurately and efficiently.
This structured approach reduces errors, ensures prompt handling, and minimises the chaos often associated with large volumes of returns. Overall, it makes the operation smoother and more predictable.
RMA systems help reduce fraudulent returns by verifying return requests and tracking returned products. Unique RMA codes and proper documentation for each return ensure that only legitimate returns are processed.
This verification process significantly reduces financial losses associated with return fraud, such as customers attempting to return products purchased from unauthorised sellers.
A well-managed RMA process helps improve customer satisfaction. Clear communication and efficient return handling build trust and loyalty.
A smooth and straightforward return process enhances the business’s reputation and encourages repeat purchases. Satisfied customers are likely to leave positive reviews and recommend the business to others.
RMA systems help businesses maintain better control over their inventory.
Tracking returned products accurately updates the inventory system in real-time, ensuring that stock levels reflect the actual inventory. This optimisation of inventory management reduces excess stock and prevents stockouts.
Efficient return management through RMA systems leads to significant cost savings.
Streamlining the return process and reducing errors lowers operational costs associated with handling returns. Identifying common return reasons through RMA data helps improve product quality and reduce return rates.
RMA systems provide valuable data on returns, which businesses can analyse to identify trends and issues. Understanding the reasons for returns helps companies address product quality problems, improve customer service, and make data-driven decisions.
Detailed return data reveals patterns, such as frequent defects in a particular product batch, enabling proactive measures to rectify issues. Enhanced visibility into return data supports strategic planning and operational improvements.
Integrating an RMA system with other business tools, such as inventory management software, creates a streamlined workflow. This integration ensures all departments have access to accurate and up-to-date information, improving coordination and efficiency.
When a customer requests return, the customer service team can quickly access the return details, the warehouse can prepare to receive the product, and the finance department can process the refund. Streamlined workflows reduce bottlenecks and enhance overall productivity.
RMA systems are essential for various types of businesses that handle product returns. Here are the key groups that can benefit from implementing an RMA system.

Return Merchandise Authorisation is essential for managing product returns effectively. It involves assigning a unique alphanumeric code to authorise and track returns, ensuring a smooth and accurate process.
RMA labels include this code, along with customer information, product details, and return instructions, making the return or exchange process more efficient.
These labels help businesses handle returns systematically, reduce errors, and enhance customer satisfaction. Implementing RMA benefits various businesses, including eCommerce platforms, retail stores, manufacturers, and service providers.
We hope this article was useful.
Thanks for reading!
In shipping, RMA stands for Return Merchandise Authorisation.
The responsibility for paying shipping costs for an RMA varies by business.
Some companies cover the shipping costs, while others require the customer to pay for return shipping.
An RMA form is a document that customers fill out to request a Return Merchandise Authorisation. It includes information such as the reason for return, product details, and customer information, helping businesses process returns accurately.
On Amazon, RMA stands for Return Merchandise Authorisation number. It is a unique number used to track return requests.
Information needed for an RMA typically includes:
Auckland
Christchurch
Phone 09 579 2057
Live Chat – Widget below
Auckland
Christchurch
Phone 09 579 2057
Live Chat – Widget below